What Is Boiling Point Elevation
sixteen.14: Boiling Point Height
- Page ID
- 53862
Table salt is ofttimes added to boiling water when preparing spaghetti or other pasta. One reason is to add season to the nutrient. Some people believe that the addition of salt increases the boiling point of the water. Technically, they are right, but the increase is rather small. Y'all would need to add together over 100 grams of \(\ce{NaCl}\) to a liter of h2o to increase the boiling point past a couple of degrees, which is probable unhealthy.
Boiling Point Elevation
The figure beneath shows the phase diagram of a solution and the upshot that the lowered vapor pressure has on the boiling point of the solution compared to the solvent. In this instance, the solution has a college boiling betoken than the pure solvent. Since the vapor pressure level of the solution is lower, more rut must exist supplied to the solution to bring its vapor pressure level up to the force per unit area of the external temper. The boiling point tiptop is the difference in temperature between the boiling signal of the pure solvent and that of the solution. On the graph, the boiling bespeak superlative is represented by \(\Delta T_b\).
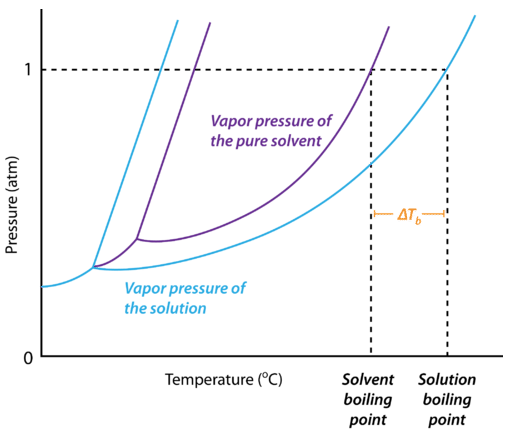
The magnitude of the boiling bespeak elevation is besides directly proportional to the molality of the solution. The equation is:
\[\Delta T_b = K_b \times \textit{yard}\nonumber \]
The proportionality constant, \(K_b\), is called the molal boiling-bespeak pinnacle constant. It is a constant that is equal to the alter in the boiling betoken for a 1-molal solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute. For water, the value of \(K_b\) is \(0.512^\text{o} \text{C}/\textit{grand}\). Then, the boiling temperature of a 1-molal aqueous solution of any nonvolatile molecular solute is \(100.512^\text{o} \text{C}\).
Summary
- Boiling point elevation is the difference in temperature between the boiling signal of the pure solvent and that of the solution.
- The molal boiling-betoken elevation constantis equal to the change in the boiling signal for a 1-molal solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute.
- Calculations involving the molal humid point summit constant are outlined.
What Is Boiling Point Elevation,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_Chemistry/Introductory_Chemistry_%28CK-12%29/16:_Solutions/16.14:_Boiling_Point_Elevation
Posted by: moorehicave.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Boiling Point Elevation"
Post a Comment