Similarities Between Fungi And Plants
R.H.Whittaker classified organisms based on several characteristics. Cellular organization, reproduction, phylogeny, mode of nutrition, etc. are taken into account. Thus, plants and fungi are classified under separate kingdoms.
Plants
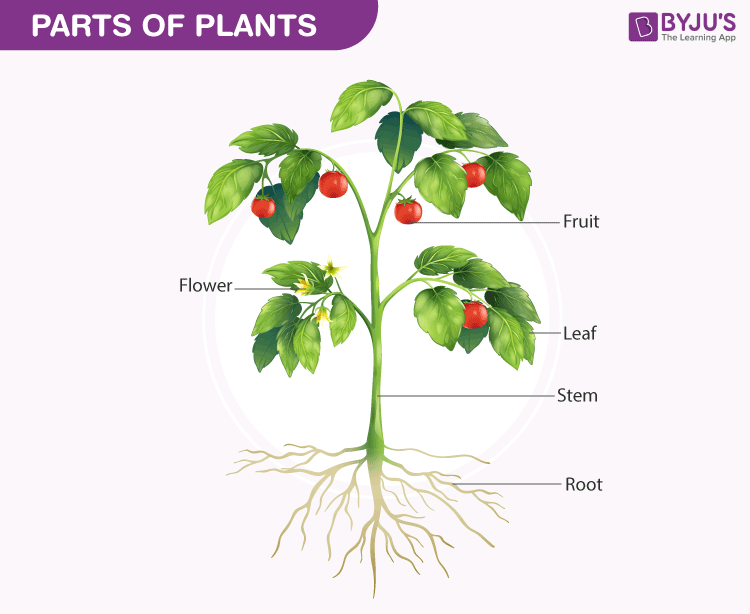
Plants are multicellular, eukaryotic autotrophs with a rigid cell wall. They take dissimilar parts for support, anchorage and photosynthesis. They have photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll, and tin can make their own food. Thus, they are considered as master producers in an ecosystem.
Fungi
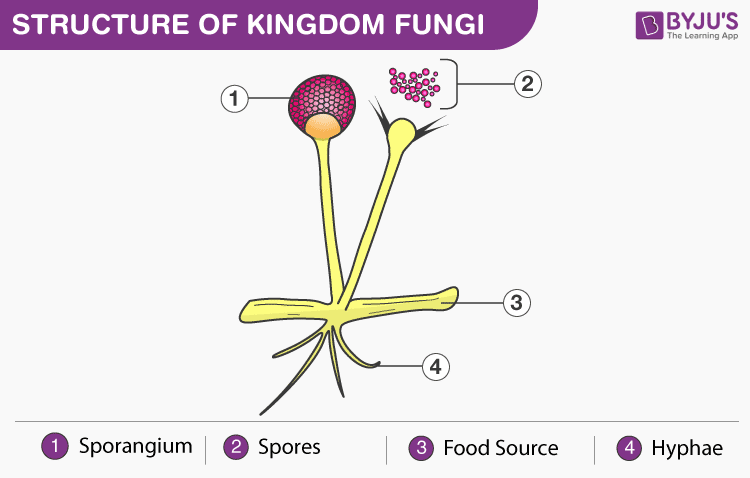
Fungi are besides eukaryotes. They include both microscopic (yeast) and macroscopic (mushrooms) organisms. Most fungi are filamentous structures. They have long thread-similar hyphae, which form a network called mycelium.
They lack chlorophyll and show a heterotrophic style of nutrition. They have a vital role in the ecosystem as decomposers. Spores are the only gametes that help in the reproduction of fungi.
Extended Reading: Kingdom Fungi
Departure between Plants and Fungi
Plants | Fungi |
| Plants are autotrophic eukaryotes. | Fungi are heterotrophic eukaryotes. |
| They are producers in a food concatenation. | They are decomposers in a food chain. |
| Their cell wall is made of cellulose. | Their cell wall is made of chitin. |
| The food is ordinarily stored as starch. | The food is stored as glycogen. |
| Plants have chlorophyll. | Fungi do not take chlorophyll. |
| Most of the plants accept roots, leaves and stems. | The fungal trunk includes hyphae (they interconnect to course mycelium). |
| Sexual reproduction – Fusion of male and female gametes happen to produce offspring. Asexual reproduction – The two major types are apomixis and vegetative propagation. | Sexual reproduction – The cytoplasm and nucleus of the two-parent cells fuse to course a gamete. They undergo meiosis to produce spores. Asexual reproduction – This happens through spores, budding or fragmentation. |
| Found kingdom classification includes – Thallophyta, Pteridophyta, Bryophyta, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms. | Kingdom fungi includes – Ascomycetes, Zygomycetes, Basidiomycetes, Deuteromycetes. |
| Examples – Kokosnoot tree, Rose plant, etc. | Examples – Molds, Mushrooms, etc. |
Also Read: Differences between Fungi and Algae
Ofttimes Asked Questions
What is mycology?
The study of fungi is termed mycology. The fungi are eukaryotes that include yeast and mushrooms. The structure and properties of fungi, along with their relationship with other organisms, are explored in mycology.
What are the similarities betwixt plants and fungi?
Both fungi and plants are eukaryotes. They do non show any movement or locomotion. Likewise, both plants and fungi accept membrane-bound nuclei.
Do fungi take chloroplast?
No, fungi exercise non have chloroplast likewise as chlorophyll. They are heterotrophic organisms. Their mode of nutrition can be symbiotic, parasitic or saprophytic. Fungi produce enzymes to interruption complex organic nutrient into its simpler forms.
What are cryptogams and phanerogams?
Cryptogams and phanerogams are classifications nether the found kingdom. Cryptogams include non-flowering plants such as bryophytes, thallophytes and pteridophytes. Phanerogams include flowering plants like angiosperms and non-flowering plants like gymnosperms.
Likewise come across: Found Kingdom Classification

Keep Exploring BYJU'South Biology for more than heady topics.
Similarities Between Fungi And Plants,
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/difference-between-plants-and-fungi/#:~:text=What%20are%20the%20similarities%20between,fungi%20have%20membrane%2Dbound%20nuclei.
Posted by: moorehicave.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Similarities Between Fungi And Plants"
Post a Comment